Recently, Prof. Sun Zhi-Jun’s team in our hospital achieved innovative achievements in the biomimetic target cancer therapy area by collaborating with Prof. Zhao Xing-Zhong and Prof. Liu Wei from School of Physics and Technology of Wuhan University. The relevant research results were published in Nature Index Journal: Advanced Functional Materials.
The title of the thesis is "Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cell Membrane-Coated Magnetic Nanoparticles for Cancer Theranostics by Inducing Macrophage Polarization and Synergizing Immunogenic Cell Death". The State Key Laboratory Breeding Base of Basic Science of Stomatology, Hubei Province & Key Laboratory of Oral Biomedicine (Wuhan University), Ministry of Education is the first completed department. Dr. Yu Guang-Tao in Department of Oral Maxillofacial-Head Neck Oncology in our hospital and Dr. Rao Lang in School of Physics and Technology of Wuhan University are the co-first authors. Prof. Sun Zhi-Jun in our hospital and Prof. Liu Wei in School of Physics and Technology of Wuhan University are the corresponding authors of this paper. The research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, National Natural Science Foundation for Outstanding Youth Foundation, and National Key Research and Development Program.

As one of the most important public health problems, the main therapeutics of cancer include surgery, radiotherapy and chemotherapy. These traditional therapeutics have limited ability to target the tumor microenvironment. Myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs) are a group of important negative immunoregulatory cells in the tumor microenvironment, inhibiting the killing ability of immune cells against tumor cells. Based on the characteristics of MDSCs, the research team first proposed the application of homologous MDSCs membranes to wrap magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles that have been approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the synthesis of active targeting tumor microenvironment composite nanoparticles MNP@MDSC.
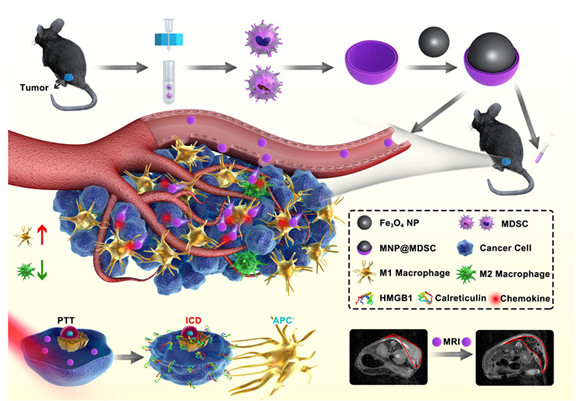
This composite nanoparticle integrates the functions of MDSC and Fe3O4 nanoparticles, exhibiting excellent anti-phagocytosis, long cycle time, the ability to actively target the tumor microenvironment, excellent photothermal therapy (PTT), nuclear magnetic resonance (MRI) imaging ability and significant anti-tumor ability. Molecular mechanism studies have found that the application of the nanoparticles for phototherapy can cause immunogenic cell death in tumor cells, promote the differentiation of M2 macrophages to anti-tumor M1, and synergistically promote the body's anti-tumor immune response. Small animal positron emission tomography (PET) detection suggests that the metabolic capacity of the tumor after MNP@MDSC nanoparticle treatment is significantly reduced, thereby inhibiting tumor growth.
In recent years, collaborating with Prof. Liu Wei’s and Prof. Guo Shi-Shang’s team, Prof. Sun Zhi-Jun’s team has achieved a number of original innovations in the field of cancer diagnosis and treatment by employing the biomimetic nanomaterials modified with red cell membrane, tumor cell membrane et al. The research results were successively published in journals such as Advanced Materials、Advanced Functional Materials、Angew. Chem. Int. Ed.、Small、Nanoscale、ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces.
Full text link:https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201801389
Dr. Yu Guang-Tao
Department of Oral Maxillofacial-Head Neck Oncology



